Technology
Zoom catches up with new accessibility features for sign language interpretation
For Zoom users who are part of the Deaf and hard-of-hearing community, some long-awaited features are here.
On Wednesday, Zoom added three major accessibility options, each mainly focused on making it easier for sign language interpreters to stay visible on the screen.
Jen Hill, a Zoom marketing manager, demonstrated on a Zoom call how users can now pin and spotlight multiple video screens at a time, to keep someone who is signing alongside the speaker or on the main screen and always in view. In Zoom’s grid view, users can rearrange video windows to keep the interpreter where they want to see them. These changes are intended so that everyone is “able to live and work in a digital platform,” especially during these pandemic days.
Following standards set through the A11Y digital accessibility group, which promotes inclusion for people with disabilities on tech tools and services, Zoom added spotlighting and pinning for multiple screens during video calls. Previously, you could only pin one video screen while on a Zoom call. For meetings (those are usually in speaker mode, which keeps whomever is speaking highlighted), users can keep more than one speaker’s video centered, so there can be several videos pinned to the main screen. Only you as the user would see the multiple videos, so you can choose to keep an interpreter video pinned next to the main speaker, while other call participants might choose to just have the speaker centered on their screens.
Zoom hosts can give multi-pinning access to up to nine different people on a call. Hill explained that it’s a resource-heavy ability intended for people who need it to see what someone is saying while on a Zoom call.
Multi-spotlight is pretty much the same thing as pinning, except the host can decide to keep up to nine videos in place for everyone to see, no matter who is speaking during the video meeting. This can help keep the sign language interpreter’s video up alongside the speaker’s. The photo at the top of the page shows what a screen with four different videos spotlighted looks like.
Then, there’s a feature in gallery view that all users — it’s not limited to only nine per a call — will be able to use starting Wednesday: You can rearrange the placement of videos. You could move the interpreter’s video box closer to the content on the screen, or order different screens as you like. This is supposed to help users keep a certain speaker or interpreter in a certain position on the screen, like closer to a presentation with graphs and charts.
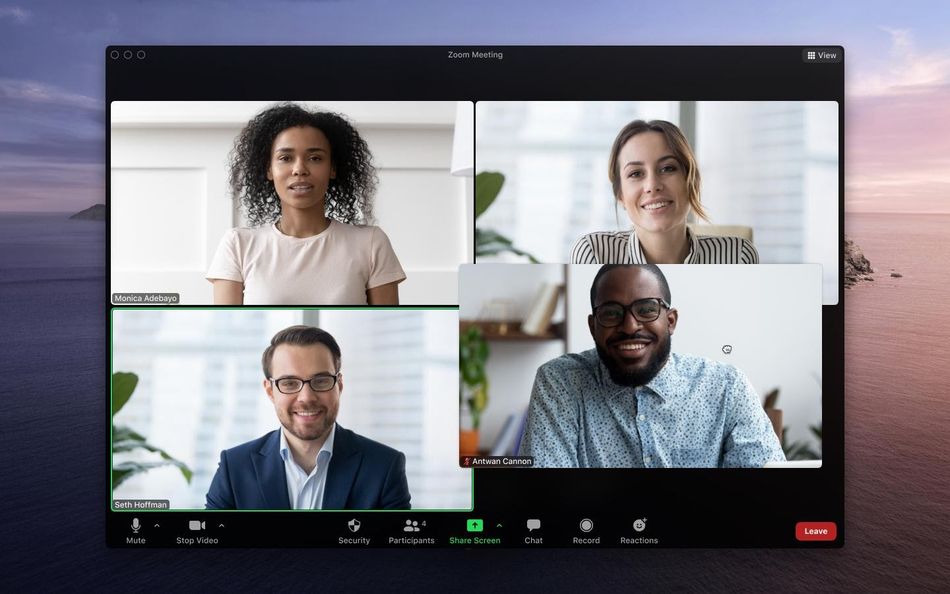
Rearrange window placement for what works best.
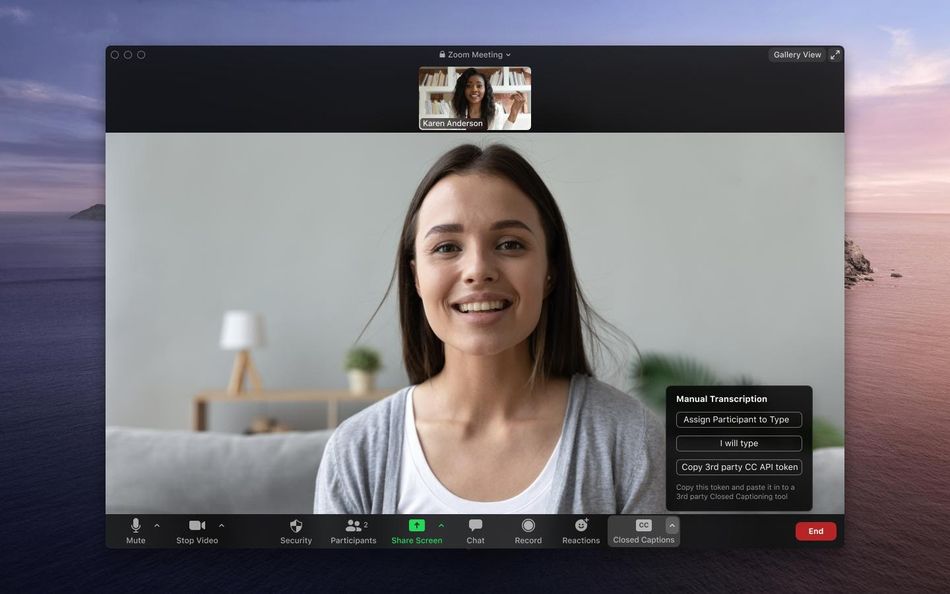
Transcribing comes with many options.
Hill summed up the additions to Zoom as ways you “can maximize control for your own particular needs.”
Looking at other video conferencing services, there are a mix of accessibility tools available. Cisco’s WebEx is by far the most comprehensive, with all of Zoom’s new features already baked into its product. Skype and Google Meet mostly provide transcription and real-time closed captioning as ways to allow users who are deaf use the services. Google Meet users have asked for something like Zoom’s new pinning option as recently as this month.
Apple’s FaceTime just got an accessibility upgrade with the release of iOS 14 last week. In group calls, FaceTime now auto-detects if someone is using American Sign Language, or ASL, and keeps that video front and center.
Zoom already offered keyboard shortcuts, screen readers, and closed captioning. As Zoom’s first chief diversity officer Damien Hooper-Campbell said in a Zoom — naturally — call, “It’s a continuous tinkering.” He and the team are “constantly learning” about how to best launch Zoom accessibility features and updates.
-
Technology4 days ago
Researchers created a sleep-tracking device designed to alter dreams — Future Blink
-
 Technology4 days ago
Technology4 days agoInstagram, YouTube, and more (UK deal)
-
Entertainment7 days ago
Netflix’s ‘Unsolved Mysteries’ Volume 2 Review: The Best Episodes
-
Technology4 days ago
Twitter is still letting you retweet. You don’t have to quote tweet.
-
Politics7 days ago
New York Post skepticism in publishing Hunter Biden stories: report
-
Featured6 days ago
Energy price cap extended until end of 2021 | Business News
-
 Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days ago98% off bundle (UK deal)
-
Politics3 days ago
Facebook oversight board debuts, but no decisions before Election Day


